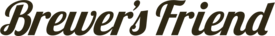Ensuring Success With Your First Lagers
Friday, March 20th, 2020By Old Standby Brewing
You’ve been homebrewing for a while now and have pumped out some pretty tasty ales, impressing the hell out of friends and family; probably some IPAs, stouts, maybe even a porter or an ESB. Now you’re thinking you might want to try your skills at a crispy lager since you’ve been seeing them pop up more and more at breweries lately. Well, here are the most important things to consider before you take on the challenge of producing a tasty lager. The 3 most important things to remember when crafting a quality lager: Yeast, Temperature, and Patience! Let’s discuss further.
Your First Lager Recipe
As far as recipe development goes, it’s best to keep it simple in the beginning. Start with a basic malt bill that uses high-quality Pilsner malt and only small percentages of 1 or 2 specialty malts. Don’t worry about step mashing for this recipe. Pick a single infusion temperature (around 150°F) and mash in just as you would with all the ales you’ve brewed. Next, collect all that sweet wort into your kettle and once again, keep your hop schedule pretty simple. Refer to the BJCP guidelines for the lager style you’re brewing and keep the IBU in the suggested range. Perhaps you’ll want to use a noble hop variety or two here to really capture those traditional aromas and flavors. Once your boil is complete, which you may want to increase to 75 or 90 minutes to help reduce some off-flavors associated with high levels of pilsner malt, try to chill as quickly as possible and transfer to your sanitized fermenter. This was the easy part! If you’re looking for a great go-to lager recipe check out the Oktoberfest recipe created by Daily_Brewer. You can also check out the recipe section for more lager recipe inspiration.
Yeast Strains For Lagers
Here’s where your lager really needs some tender love and guidance to reach its full potential. Since lager yeast moves slower & does its best work at cooler fermentation temperatures, you’re going to want to pitch at least double (or maybe triple) the amount you normally pitch into your ales. This yeast also needs to be fresh so check the packaging dates. I try to use yeast that is dated within 1-2 months of my brew date. If you can’t get super fresh yeast, you’ll either want to purchase more or make a starter to get your yeast ready to tackle your lager. Remember, the yeast is doing all the work here, so make sure you’re adding enough to make your first lager attempt successful. I find that the pitch rate calculator on Brewer’s Friend is an excellent resource to determine how much yeast I actually need to use. It’s better to pitch more viable, healthy cells than not enough!
Lagers And Temperature Control
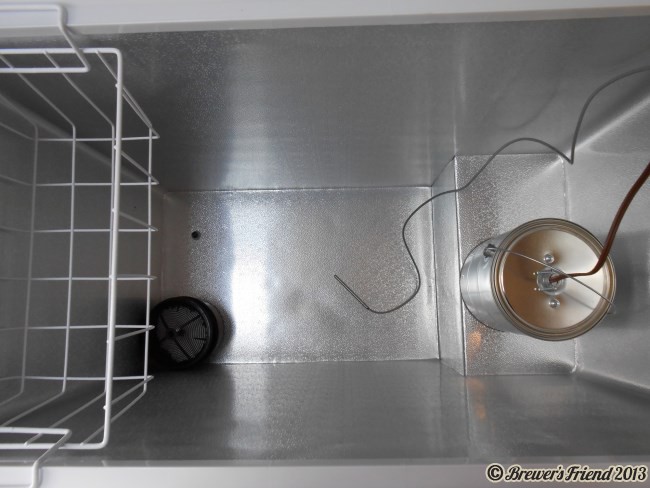
Now that you’ve brewed the beer and pitched plenty of fresh lager yeast, it’s time to create the optimum fermentation environment for your lager yeast to do the important work it needs to do. In order to create a choice lager, you have to be able to keep your fermenter at consistent lager temperatures for a long period of time. This means in the range of 48-52°F for 2 weeks and then down to almost freezing temps for a month or more. Each variety of yeast that you use will have an optimum fermentation range so use this information as your guide. If you don’t have the ability to control your fermentation temperature yet, you may want to consider not brewing a lager at this point in your homebrewing career. Sorry for the brutal honesty here, but I’m just trying to save you the heartache of your lager not turning out very good!
Stay Patient With Your Lagers
Sticking with the theme of keeping it simple, hold this temperature for at least 7-14 days before you do anything. Now, you’re going to be used to the activity that you’ve seen from your ale fermentations; you’ve possibly even blown a few airlocks off the top of your carboy, right? Well, lager fermentation happens much slower. Picture the sloth DMV scene in Zootopia or maybe even your last service call with your utility company! I digress. There are a few very well-known techniques for attempting to speed up your lager fermentation by some very well respected brewers, but I would urge you to keep it simple for your first lager and stick to a basic fermentation schedule which takes a few more days, but is less complex and doesn’t require you to take a bunch of gravity readings. Once your lager activity starts to really slow down after 7-14 days, raise the temperature of your fermentation vessel a few degrees, to the upper end of the range that we talked about earlier from the yeast manufacturer, and hold at this temp for at least another 3-4 days. This warming at the end of the fermentation will give your yeast a chance to clean up any off-flavors that have been produced. This is also known as a diacetyl rest. Diacetyl is a buttery flavor that you don’t want in your finished lager so be patient and give the yeast a chance to tidy things up. If you’re still seeing some activity in your blow-off, take a gravity reading to see if your lager is getting close to being finished. If not, give the beer a few more days to wrap things up.
Packaging Your Lagers
When all activity in your fermenter has stopped and you’ve hit your final gravity, it’s time to start cooling your beer down to start the lagering process. The word lager, or lagern in German, means “to store” or “to keep,” so really you’re just beginning to create the amazing flavors that you’ve come to love from a crispy lager. Lower the temperature of your fermenter about 2-3 degrees per day (patience, remember?) until you get down to 32-35°F and hold at this temp for as long as you can possibly stand it! Usually, 3-4 weeks is a good lagering time, but some of the more powdery yeast strains will need longer to drop out of suspension completely and some higher alcohol lager varieties will need even more time to fully mature. It is best to do this lagering phase with all of your yeast still in the fermenter, so don’t worry about racking into a secondary fermenter at this time. This allows your lager yeast to continue working its magic and creating the delicate flavors that you’ll want in your finished beer.
Now that you’ve completed your lagering stage you’re probably really thirsty and hopefully, you brewed enough ales before this lager to get you through the last couple of months! If you have the ability to keg and force carbonate your lager, you could be enjoying pints in just a few days. If you bottle condition your beer, then you’re going to have to wait a couple more weeks for your lager to fully carbonate. Bottle carbonation happens when the remaining yeast in your beer consumes the priming dextrose that you add at bottling, but since you’ve just finished a month-long lagering phase, there isn’t too much yeast left in your beer. So once again be patient because carbonation will take longer than usual. I probably don’t have to remind you, but I will anyway since you’ve come this far, sanitation is so important when making quality beer after your boil is complete. When you make a lager there is nowhere for off-flavors to hide, so make sure you’re cleaning and sanitizing everything that will come in contact with your beer once it leaves your boil kettle.
When it comes time to pour the first pint of lager that you crafted and cared for over the last couple of months, you’re going to have a new appreciation for lager brewing. Pay close attention to the delicate and subtle flavors of the pilsner malt and the traditional aromas of the German hops. Planning your next lager is a great thing to do while you enjoy your first few pints of the brew you just completed! Prost!